Cross-chain bridges are the lifeblood of blockchain interoperability in 2025, empowering users to move assets and data seamlessly across an ever-expanding web of networks. Yet, as anyone following DeFi headlines knows, these same bridges have become prime targets for attackers. Why do so many cross-chain bridge security models fail, even as the industry pours billions into audits and infrastructure upgrades? The answer lies in a mix of centralization risks, technical complexity, and misplaced trust assumptions.

Why Traditional Cross-Chain Bridges Keep Failing
The core flaw in most cross-chain bridge designs is centralization. While blockchains themselves are decentralized by design, many bridges rely on a small group of validators or multisig wallets to approve transfers. This creates a tempting single point of failure. If attackers compromise just a handful of these validators, or collude with them, they can drain the entire bridge vault. It’s happened before, and without changes to trust models, it will happen again.
Recent studies highlight three recurring vulnerability themes:
- Centralization Risks: Bridges managed by centralized entities or limited validator sets are vulnerable to insider attacks and governance failures.
- Smart Contract Bugs: Complex bridging logic is notoriously difficult to audit. Even minor bugs can lead to catastrophic exploits, think unbacked token minting or unauthorized fund releases.
- Custodial and Economic Risks: Most bridges lock assets on one chain while issuing wrapped tokens on another. If the custody contract is compromised, those wrapped tokens instantly lose value.
This isn’t just theory, billions have been lost to bridge hacks over the past few years. Want more details on how trust models create hidden risks? Check out this deep analysis for developers.
The Push for Trust-Minimized Blockchain Architectures
The solution isn’t to abandon bridges altogether but to rethink their architecture from first principles. In 2025, leading projects are shifting toward trust-minimized blockchain architectures. Here’s what that looks like in practice:
- Decentralized Validator Networks: Instead of relying on five multisig holders in a Telegram group chat, new designs use hundreds (or thousands) of distributed validators. This drastically reduces the odds that attackers can compromise enough participants for an exploit.
- Formal Verification and Rigorous Auditing: Smart contracts now undergo mathematical proofs and multiple independent audits before going live, a huge step up from quick code reviews of years past.
- On-Chain Validation Mechanisms: Modern bridges increasingly leverage cryptographic proofs (like zk-SNARKs) and robust rate limits to catch suspicious transactions before they cause harm.
If you’re curious about how threshold signature schemes (TSS) and multi-party computation (MPC) are changing the game for bridge security, this resource is worth a read: How MPC and TSS enhance cross-chain bridge security.
The Ongoing Battle: Attackers vs Bridge Defenders
No matter how advanced our tools become, attackers continue evolving right alongside us. Many recent hacks have exploited not just code bugs but also social engineering, tricking validators or exploiting governance loopholes to gain control over critical infrastructure. That’s why leading protocols now deploy automated monitoring systems that scan for anomalies in real time and trigger incident responses within seconds.
This arms race isn’t slowing down any time soon. For developers building or integrating with bridges today, understanding both technical vulnerabilities and human factors is non-negotiable if you want your project, and your users’ funds, to survive the next wave of attacks.
But what does a truly secure, trust-minimized cross-chain bridge look like in practice? The devil is in the details, and the best projects are layering multiple lines of defense. Let’s break down how these next-gen architectures are setting new standards for cross-chain bridge security in 2025.
Top Trust-Minimized Cross-Chain Bridges & Their Security Features (2025)
-
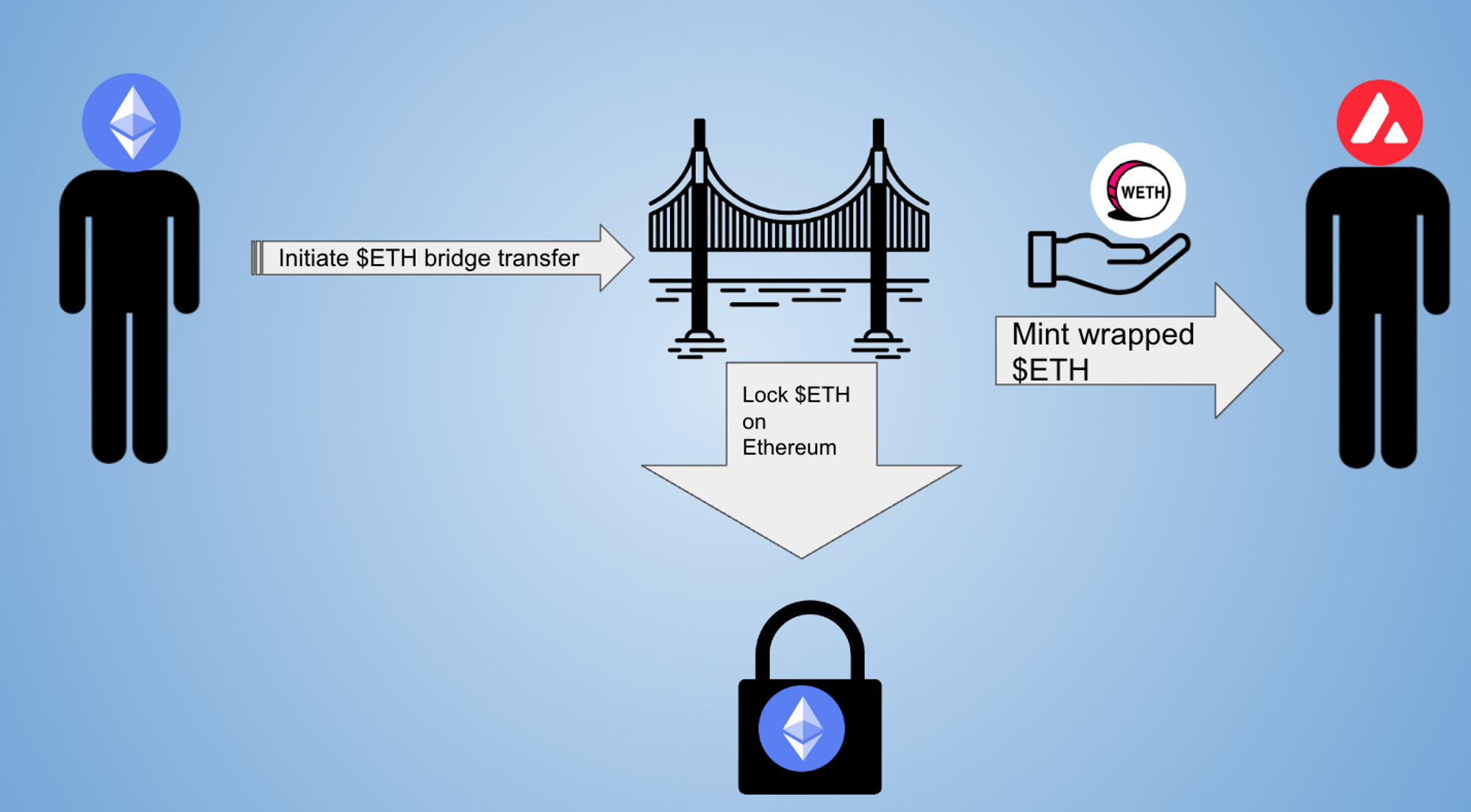
LayerZero: Omnichain interoperability protocol using Ultra Light Nodes (ULN) for decentralized validation. LayerZero minimizes trust by requiring both an oracle and a relayer to independently confirm transactions, reducing single points of failure.
-

Axelar Network: Features a decentralized validator set running on Proof-of-Stake. Axelar’s on-chain voting and cryptographic proofs ensure that no centralized party controls the bridge, and all transactions are validated by a diverse, global network.
-
Wormhole: Utilizes a Guardian network of 19+ independent validators to secure cross-chain transfers. Its real-time monitoring and rapid incident response have been upgraded post-2022, making it one of the most resilient bridges in 2025.
-

Chainlink CCIP (Cross-Chain Interoperability Protocol): Employs decentralized oracle networks for secure message delivery and transfer validation. Chainlink CCIP’s multi-layered security includes rigorous audits and formal verification, setting a new standard for trust-minimized interoperability.
-

Synapse Protocol: Combines multi-party computation (MPC) and decentralized validator networks for secure, non-custodial bridging. Synapse’s on-chain verification and automated monitoring further reduce risk of exploits.
Blueprints for Safer Bridges: Practical Steps Developers Are Taking
For teams building or integrating bridges, adopting a trust-minimized approach isn’t just about swapping out a few lines of code. It’s about fundamentally rethinking risk from every angle, technical, economic, and social. Here’s how forward-thinking protocols are raising the bar:
- Validator Diversity: The more diverse your validator set (across geography, hardware, and governance), the harder it is for attackers to coordinate an exploit.
- Continuous Audit Loops: Treat audits as an ongoing process, not a one-time checkbox. Integrate bug bounty programs and formal verification into your development pipeline.
- Permissionless Participation: Allowing anyone to become a validator (with sufficient economic stake) reduces collusion risk and increases transparency.
- Automated Incident Response: Deploy bots that freeze suspicious transactions or trigger emergency governance votes when anomalies are detected.
If you want a deeper dive into how trust assumptions create hidden risks, and how to spot them, this resource is essential reading: How Trust Assumptions in Cross-Chain Bridges Create Security Risks.
Why User Education Matters More Than Ever
No amount of cryptography can save users from poor decisions if they don’t understand the risks behind each bridge. In 2025, we’re seeing leading bridges invest heavily in transparency, think real-time dashboards showing validator health, up-to-date audit statuses, and clear documentation on how funds are secured. Users now expect to see at-a-glance whether they’re interacting with a light client bridge or a custodial solution, and what that means for their assets’ safety.
The rise of community-driven monitoring tools and open-source risk scanners empowers users to verify claims for themselves. This collective vigilance is already making it harder for bad actors to hide systemic weaknesses until it’s too late.
The Road Ahead: Building Bridges Worth Trusting
The future of blockchain interoperability hinges on one thing: earning user trust through transparent, resilient design. Every protocol upgrade, every new validator added, every audit published is another brick in that foundation. If you’re working on cross-chain technology, or just using it, demand more than buzzwords like “decentralized” or “trustless. ” Insist on evidence: open audits, permissionless participation, robust monitoring systems.
The stakes have never been higher. Billions ride on these rails every day, and attackers aren’t taking weekends off. By embracing trust-minimized architectures now, we can build bridges that not only connect chains but also inspire confidence across the entire ecosystem.
If you want practical frameworks for evaluating bridge security yourself (or assessing third-party integrations), check out our deep-dive here: How to Evaluate Cross-Chain Bridge Security: A Practical Risk Assessment Framework.












