Cross-chain bridges are the lifeblood of multi-chain DeFi, but in 2024, they also became the industry’s biggest liability. With over $2.8 billion stolen in bridge hacks last year alone, the urgency to rethink bridge security is at an all-time high. As we head into 2025, a new generation of trust-minimized architectures is emerging, aimed at making these catastrophic exploits a thing of the past.

Why Cross-Chain Bridges Have Been Hacker Honeypots
To understand why cross-chain bridge security in 2025 is such a hot topic, we need to look at how bridges traditionally worked. Most early bridges relied on centralized or semi-centralized custodians, entities or multisigs holding users’ assets while messages were relayed between chains. This setup created massive single points of failure. Attackers only needed to compromise these custodians or exploit smart contract bugs to drain hundreds of millions in minutes.
The scale and frequency of attacks exploded as DeFi matured and TVL (Total Value Locked) soared across ecosystems. From smart contract vulnerabilities to compromised validator sets, the attack surface was huge, and hackers took full advantage.
If you want a deep dive into why these trust assumptions create hidden risks, check out this analysis on trust models in cross-chain bridges.
The Rise of Trust-Minimized Bridge Architectures
The solution? Remove as much trust as possible from the equation. Trust-minimized bridges don’t rely on any single party or small group to secure user funds. Instead, they harness cryptographic proofs (like zero-knowledge proofs and light client verification), decentralized validator sets, and automated monitoring to make attacks dramatically harder.
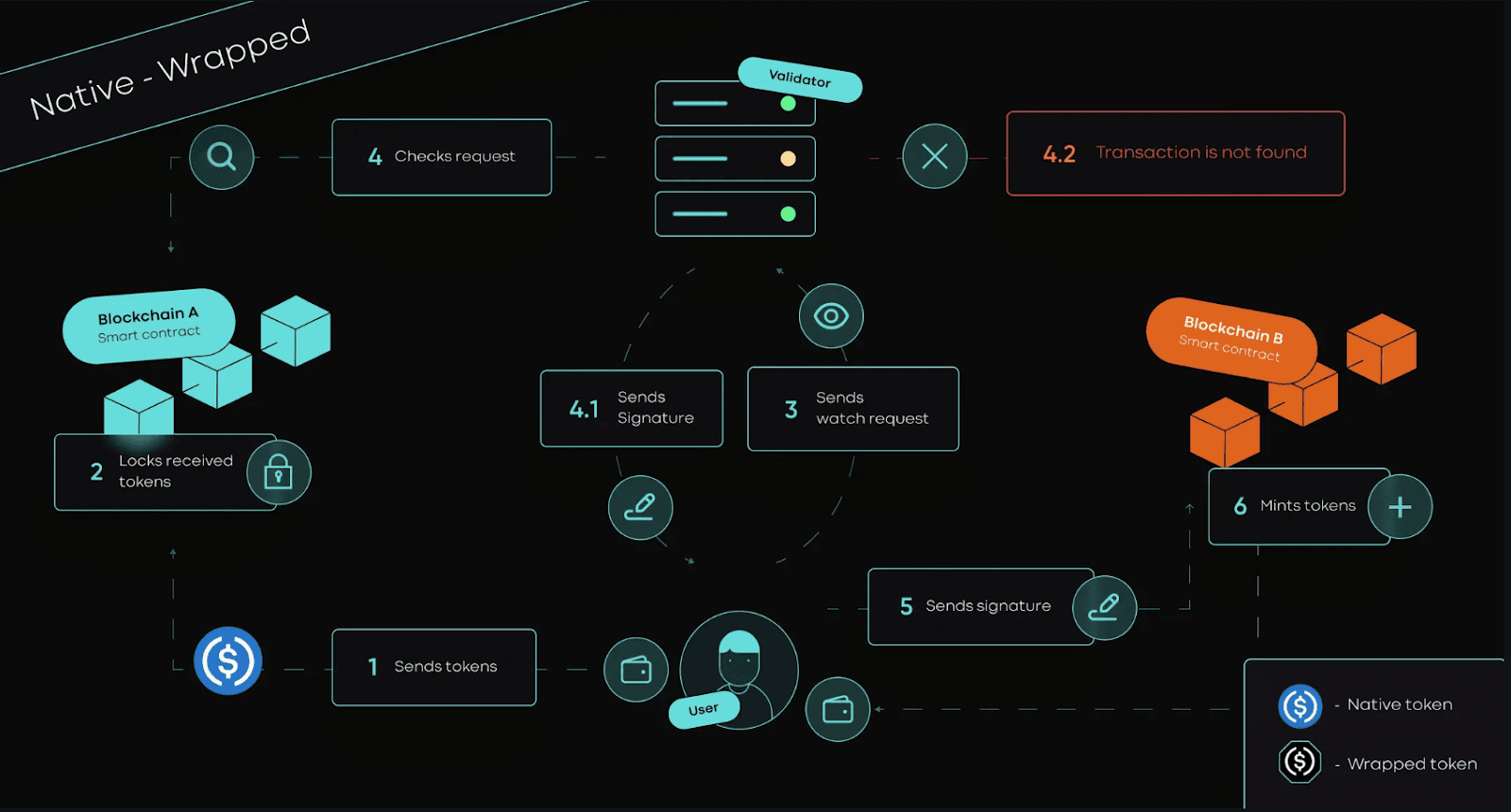
deBridge, for example, leads with a zero-TVL architecture, meaning user funds aren’t pooled in vulnerable contracts at all, and boasts zero exploits after 26 and audits. Protocols like Union are pushing trust-minimized Bitcoin bridging using clever cryptography rather than centralized custody.
This shift isn’t just theoretical; it’s showing real results. The best bridges now combine:
- Light client verification: Bridges validate transactions directly against source chain data, no middlemen required.
- Decentralized guardians: Large sets of independent actors validate and relay messages, reducing collusion risks.
- MPC and TSS: Multi-party computation and threshold signatures split signing authority across many parties for robust resilience.
If you’re curious about how MPC and TSS work under the hood for bridge defense, see our guide on enhancing bridge security with MPC and TSS.
Pioneering Security Innovations: V-ZOR, ConneX and BridgeShield
The arms race between attackers and defenders has driven some remarkable innovation this year:
- V-ZOR: A verifiable oracle relay that fuses zero-knowledge proofs (Halo 2) with quantum entropy for unpredictable validator selection, making oracle manipulation all but impossible.
- ConneX: An AI-powered system that automatically links corresponding transactions across chains for seamless fund tracing and vulnerability detection.
- BridgeShield: Uses advanced graph neural networks to map complex cross-chain behaviors and flag suspicious activity with industry-leading precision.
Together, these tools are raising the bar for detection, auditability, and real-time response. For developers building or integrating with bridges in 2025, leveraging these technologies is quickly becoming table stakes, not just nice-to-haves.
The New Best Practices: Securing Bridges Before Hackers Strike
No security paradigm is perfect, but by combining trust-minimized design with vigilant operations, teams can drastically cut risk exposure. Here’s what leading protocols are doing right now:
- Active Monitoring and Rapid Response: Real-time scanning tools spot anomalies before they become exploits.
- Capped Transaction Sizes: Even if an exploit occurs, losses are limited by design-imposed ceilings on transfers.
- User Education and Transparency: Users get clear warnings about risks, and actionable steps to protect themselves when using bridges.
This proactive approach is essential as attackers grow more sophisticated each year. If you’re interested in operational strategies that actually work under pressure, see our research on real-time monitoring for bridge risk mitigation.
But even the best technical defenses must be paired with robust community and ecosystem coordination. In 2025, bridge teams are forging partnerships with major exchanges to track and freeze stolen funds before they can be laundered. This kind of cross-sector collaboration, once rare, is now a critical layer in the new security stack. Pause functions: the ability to temporarily halt bridge operations at the first sign of trouble, have become standard, giving defenders precious time to investigate and respond without risking further losses.
Top Trust-Minimized Cross-Chain Bridges & Their Security Features (2025)
-

deBridge: Renowned for its zero exploits record, deBridge employs a zero-TVL architecture that eliminates common attack vectors. With 26+ independent audits, it stands out for prioritizing decentralized validation and non-custodial asset transfers.
-
V-ZOR (Verifiable Oracle Relay): This innovative bridge integrates zero-knowledge proofs (Halo 2) and quantum-grade randomness for secure, trust-minimized cross-chain communication. Its unpredictable reporter selection mitigates oracle manipulation risks.
-

Union: A trust-minimized protocol enabling secure transfers between Bitcoin and other blockchains, Union leverages decentralized multi-signature schemes and cryptographic proofs to eliminate centralized custodians and reduce single points of failure.
-

BridgeShield: This security framework uses heterogeneous graph attention networks to model cross-chain behaviors and detect attack patterns. BridgeShield achieved a high F1-score in real-world cross-chain attack detection, making it a leader in proactive bridge security.
-

ConneX: ConneX automates the identification of corresponding transactions across bridges using large language models, enhancing security analysis and fund tracing. This transparency aids in rapid vulnerability detection and response.
Transparency is also getting a long-overdue upgrade. Projects are publishing detailed post-mortems after incidents, open-sourcing audit results, and providing users with step-by-step guides for safe bridging. Real-time dashboards powered by cross-chain messaging risk scanners now alert users to live threats or suspicious activity before they interact with a bridge. This shift toward radical openness not only builds trust but also crowdsources vigilance across the entire DeFi community.
The Future of Cross-Chain Bridge Security
As protocols like deBridge continue their zero-exploit streaks and innovations like V-ZOR and BridgeShield gain adoption, the narrative is shifting from inevitability of hacks to credible prevention. Yet, staying ahead requires continuous evolution, attackers are already probing for weaknesses in even the most advanced trust-minimized designs. That’s why leading teams are investing heavily in blockchain bridge audit tools, bug bounty programs, and ongoing research into quantum-resistant cryptography.
The next frontier? Seamless UX that doesn’t compromise on safety. In 2025, user journeys across chains remain complex and sometimes confusing, a pain point attackers still exploit through phishing or social engineering. The goal now is to make secure bridging as intuitive as using a single-chain DEX or wallet, closing off human error as an attack vector.
If you’re building or using bridges this year, remember: no single tool or design pattern eliminates all risk. Security comes from layered defenses, technical innovation, operational excellence, real-time monitoring, transparent communication, and active user education working together. For more on why cross-chain bridges remain DeFi’s biggest risk (and how prevention strategies are evolving), read our deep dive here.
The bottom line? While multi-billion dollar hacks rocked DeFi in 2024,2025’s rapid evolution toward trust-minimized bridge architecture is proving that resilient interoperability is possible, if we stay vigilant and keep innovating together.






